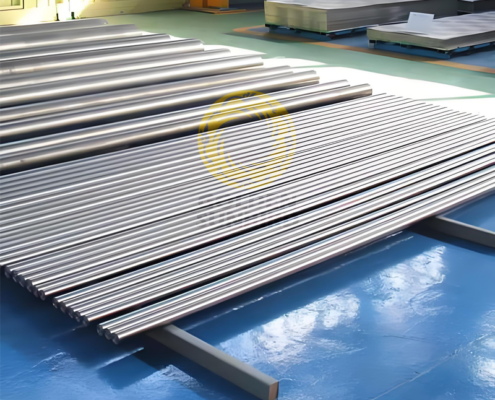
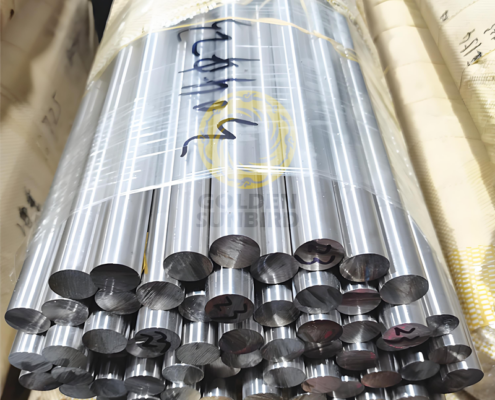
Golden Sunbird Metals is a leading Chinese supplier of stainless steel bars and offers a versatile selection in various grades designed to meet the specific demands of industries worldwide. Our stainless steel bar products are renowned for their high-temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for critical applications in aerospace, oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, marine engineering, automotive, medical devices, and more. If you want to purchase stainless steel bars in bulk or need customized solutions, please don’t hesitate to contact [email protected] for a personalized quote and guidance.
FAQs
What types of Stainless Steel Bars does Golden Sunbird Metals offer?
Golden Sunbird Metals offers a wide range of stainless steel bars, including 304/304L, 310S, 316/316L, 347, N08904, S32205, S32750, S32760, and more. Each stainless steel bar type has unique properties tailored for specific applications in industries such as aerospace, chemical processing, and marine engineering.
How can I determine which stainless steel bar is right for my project?
Choosing the right stainless steel bar for your project involves considering several factors related to the material properties, project requirements, and specific application needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine the appropriate stainless steel bar:
- Define your mechanical, corrosion, and temperature resistance requirements.
- Select the appropriate grade of stainless steel.
- Choose the bar shape and size that fits your application.
- Decide on the surface finish based on aesthetic and functional needs.
- Consider environmental conditions and fabrication requirements.
- Balance your budget with the material performance.
- Seek expert advice for optimal material selection.
Can Golden Sunbird Metals provide custom sizes for stainless steel bars?
Yes, Golden Sunbird Metals can provide custom sizes for stainless steel bars. Customization is a common service offered by us to meet specific project requirements. Here’s how they typically handle custom size requests:
Customization Options
- Dimensions:
- Length: Stainless steel bars can be cut to custom lengths as per your requirements.
- Diameter/Thickness: Custom diameters and thicknesses can be specified for round, square, flat, and other-shaped bars.
- Width: Custom widths are available for flat and rectangular bars.
- Shapes:
- Custom shapes beyond standard round, square, flat, hexagonal, angle, channel, rebar, and T-bars can often be fabricated to meet unique design needs.
- Surface Finish:
- Custom finishes, including specific polish levels or special treatments like brushed or mirror finishes, can be requested.
- Material Grades:
- Specific grades of stainless steel can be provided based on the application requirements, including but not limited to 304, 316, 410, 420, and 430.
Process for Ordering Custom Sizes
- Specification Submission:
- Provide detailed specifications for the required custom sizes, including dimensions, grade, finish, and any other relevant details.
- Quotation:
- Golden Sunbird Metals will typically provide a quotation based on the specifications provided. This will include pricing, lead time, and any minimum order quantities.
- Approval and Order Confirmation:
- Once the quotation is approved, an official order is placed. This may involve confirming all specifications and any special instructions.
- Manufacturing:
- The custom stainless steel bars are manufactured according to the agreed specifications. This may involve cutting, shaping, finishing, and quality checks.
- Quality Assurance:
- The custom bars undergo quality assurance checks to meet the specified dimensions and properties.
- Delivery:
- The finished custom-sized stainless steel bars are packaged and delivered per the agreed timeline.
What industries commonly use stainless steel bars?
Stainless steel bars are widely used across various industries due to their strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Here are some of the industries that commonly utilize stainless steel bars:
1. Construction and Architecture
- Applications: Structural components, beams, columns, and reinforcement bars (rebar) for concrete structures.
- Reason: Stainless steel’s durability and corrosion resistance are ideal for indoor and outdoor construction projects, including skyscrapers, bridges, and architectural features.
2. Automotive
- Applications: Shafts, exhaust systems, fasteners, and engine components.
- Reason: Stainless steel provides strength and resistance to high temperatures and corrosion, enhancing vehicle longevity and performance.
3. Aerospace
- Applications: Aircraft structural components, fasteners, and engine parts.
- Reason: The aerospace industry requires materials that offer high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and durability under extreme conditions, all of which stainless steel provides.
4. Marine
- Applications: Boat fittings, propellers, fasteners, and structural components.
- Reason: Saltwater makes the marine environment highly corrosive, and stainless steel’s superior corrosion resistance is crucial for long-lasting marine equipment and structures.
5. Medical and Pharmaceutical
- Applications: Surgical instruments, medical implants, diagnostic equipment, and pharmaceutical processing equipment.
- Reason: Stainless steel is biocompatible, easy to sterilize, and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
6. Food and Beverage
- Applications: Processing equipment, storage tanks, piping, kitchenware, and cutlery.
- Reason: The food and beverage industry requires hygienic materials, easy to clean and corrosion-resistant from food acids and cleaning agents.
7. Chemical and Petrochemical
- Applications: Reactors, heat exchangers, piping, and storage tanks.
- Reason: Stainless steel’s ability to withstand harsh chemicals and high temperatures makes it ideal for chemical processing and petrochemical applications.
8. Oil and Gas
- Applications: Drilling equipment, pipelines, valves, and offshore platforms.
- Reason: The oil and gas industry demands materials that endure extreme conditions, including high pressure, high temperature, and corrosive environments.
9. Manufacturing and Machinery
- Applications: Machine components, gears, shafts, and tools.
- Reason: Stainless steel’s strength and wear resistance suit high-stress applications in manufacturing and industrial machinery.
10. Power Generation
- Applications: Turbine blades, boiler components, and nuclear reactor parts.
- Reason: Stainless steel is used in power generation due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
11. Renewable Energy
- Applications: Components for wind turbines, solar panel supports, and hydroelectric equipment.
- Reason: The renewable energy sector requires durable and corrosion-resistant materials to ensure long-term performance in varying environmental conditions.
12. Textile and Pulp & Paper
- Applications: Processing equipment, rollers, and drying cylinders.
- Reason: These industries need materials that can withstand constant exposure to moisture, chemicals, and wear.
13. Electronics and Electrical
- Applications: Connectors, springs, and electronic enclosures.
- Reason: Stainless steel’s non-magnetic properties and corrosion resistance make it suitable for electronic and electrical applications.
Is your stainless steel bars environmentally friendly?
Stainless steel bars are considered environmentally friendly for several reasons, particularly sustainability, recyclability, and overall environmental impact. Here are some key points that highlight the eco-friendliness of stainless steel bars:
1. High Recyclability
- Infinite Recyclability: Stainless steel can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties. This reduces the need for raw material extraction and minimizes waste.
- Recycled Content: A significant proportion of stainless steel produced today contains recycled material, which lowers the environmental footprint associated with mining and processing new raw materials.
2. Durability and Longevity
- Extended Lifespan: Stainless steel’s resistance to corrosion, staining, and wear means it has a long service life, reducing the frequency of replacements and conserving resources.
- Low Maintenance: Due to its durability, stainless steel requires less maintenance and fewer resources over its lifecycle than other materials.
3. Energy Efficiency in Production
- Advancements in Technology: Over time, the production of stainless steel has become more energy-efficient, with technological advancements reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
- Waste Reduction: Modern stainless steel production techniques aim to minimize waste and optimize resource use.
4. Environmental Impact of Raw Materials
- Chromium and Nickel: While extracting raw materials like chromium and nickel has environmental impacts, these are mitigated by the high recyclability of stainless steel, reducing the demand for virgin materials.
- Responsible Sourcing: Many stainless steel producers are committed to responsible sourcing practices, reducing mining operations’ environmental and social impacts.
5. Application Benefits
- Hygienic Properties: Stainless steel’s non-porous surface resists bacteria and is easy to clean, making it ideal for applications in healthcare, food processing, and pharmaceuticals where hygiene is critical.
- Reduction in Harmful Chemicals: Its corrosion resistance means fewer chemicals are needed for cleaning and maintenance, reducing the release of harmful substances into the environment.
6. End-of-Life Management
- Closed-Loop Recycling: Stainless steel products are often collected and recycled at the end of their life, contributing to a circular economy and minimizing landfill waste.
- Economic Value of Scrap: The high value of stainless steel scrap incentivizes recycling and reduces the likelihood of it ending up in landfills.
Overall Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Environmental Footprint: When considering the entire lifecycle, including production, use, and end-of-life recycling, stainless steel has a relatively low environmental footprint compared to other materials.
- Sustainable Material Choice: Stainless steel’s durability, recyclability, and low maintenance requirements make it a sustainable choice for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
Stainless steel bars are environmentally friendly due to their high recyclability, durability, and advances in energy-efficient production methods. By choosing stainless steel, industries contribute to a more sustainable future, benefiting from a material that balances performance with environmental responsibility.
Can stainless steel bars be welded or machined?
Yes, stainless steel bars can be welded and machined, making them versatile for various applications. Here’s an overview of the processes and considerations involved in welding and machining stainless steel bars:
Welding Stainless Steel Bars
Common Welding Methods:
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding:
- Usage: Preferred for thin sections and high-precision work.
- Advantages: Produces high-quality, clean welds with good control over heat input.
- Considerations: It requires skill and precision; it is a slower process.
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding:
- Usage: Commonly used for thicker sections and industrial applications.
- Advantages: Faster than TIG welding, easier to learn, suitable for various thicknesses.
- Considerations: It can produce more spatter and may require more cleanup.
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) or Stick Welding:
- Usage: Often used in construction and maintenance.
- Advantages: Versatile and portable, can be used outdoors.
- Considerations: More spatter and slag, which requires cleanup; less precision than TIG or MIG.
- Laser Welding:
- Usage: Used for precision applications and in automated systems.
- Advantages: High precision, minimal heat distortion, and fast.
- Considerations: Expensive equipment requires precise control.
Welding Considerations:
- Material Grade: Different grades of stainless steel may require specific filler materials and welding techniques to avoid cracking and corrosion.
- Heat Control: Stainless steel has a low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion, making heat control crucial to avoid warping and distortion.
- Post-Weld Treatments: Depending on the application, post-weld treatments like annealing or passivation may be necessary to restore corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
- Shielding Gas: Inert gases like argon or a mix of argon and helium are commonly used to protect the weld area from oxidation.
Machining Stainless Steel Bars
Common Machining Processes:
- Turning:
- Usage: Used to create cylindrical parts and features.
- Tools: Typically performed on a lathe with carbide or high-speed steel (HSS) tools.
- Considerations: Requires appropriate cutting speeds and feeds to avoid work hardening and tool wear.
- Milling:
- Usage: Used for creating flat surfaces, slots, and complex shapes.
- Tools: End mills and face mills are used on milling machines.
- Considerations: Adequate coolant is essential to prevent overheating and prolong tool life.
- Drilling:
- Usage: Creating holes in the material.
- Tools: Carbide or HSS drill bits.
- Considerations: Use slow speeds and steady pressure to avoid work hardening and ensure clean cuts.
- Grinding:
- Usage: Finishing process to achieve a high surface quality.
- Tools: Abrasive wheels or belts.
- Considerations: Requires coolant to minimize heat buildup and maintain material integrity.
Machining Considerations:
- Tool Material and Coatings: Carbide tools with appropriate coatings (like TiAlN or AlTiN) are recommended for better wear resistance and performance.
- Cutting Speeds and Feeds: Lower speeds and higher feeds help prevent work hardening and reduce tool wear.
- Coolant Use: Ample coolant is necessary to dissipate heat and prevent thermal expansion and tool wear.
- Rigidity: Ensuring the rigid machine setup helps achieve better accuracy and surface finish.
- Work Hardening: Stainless steel tends to work harden, so consistent and adequate cutting pressure is necessary to avoid hardening the material ahead of the cutting tool.
Conclusion
Stainless steel bars are highly machinable and weldable, using appropriate techniques and considerations. Choosing the right method, controlling heat, and using proper shielding gases are critical for welding. For machining, using the correct tools, maintaining proper cutting conditions, and applying adequate coolant are essential for achieving high-quality results. These considerations allow stainless steel bars to be effectively used in various applications.