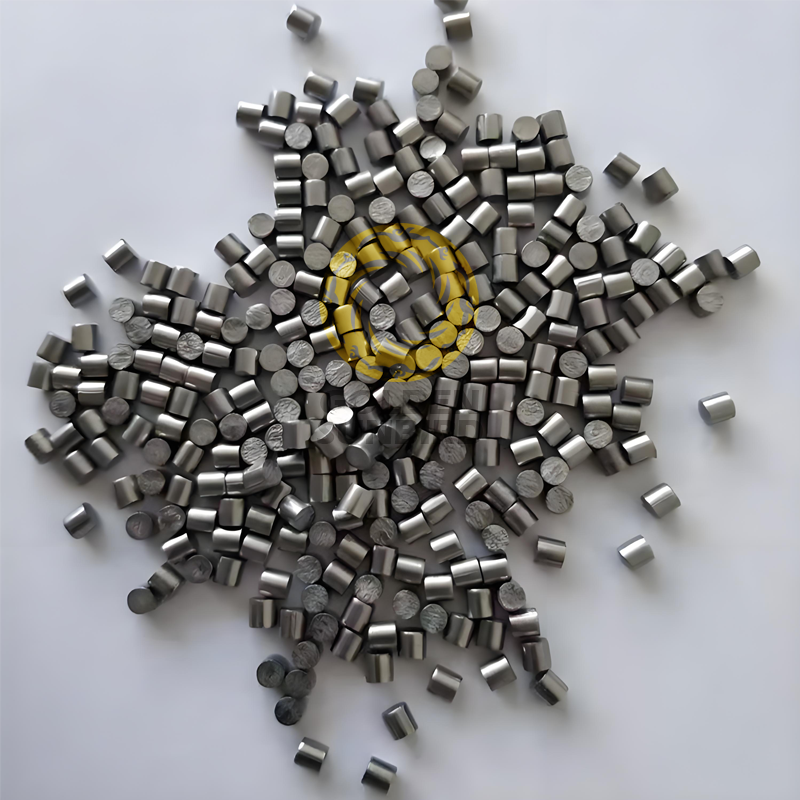
ASTM B737 Hafnium Rod, Wire, and Particles
- Type: Rod, Wire, Particles
- Rod Dia: 6 – 120 mm, Length: ≤6000mmm
- Wire Dia: 0.5 – 9.5mm (Straight Wire, Coiled Wire, Coiled on Spools)
- Particle Dia: 6 – 25mm x Length 10-30mm
- Hot-Rolled, Cold-Finished
Features
ASTM B737 Hafnium Rod, Wire, and Particles
Chemical Composition (wt.%)
| Element | Grade R1 (Nuclear Grade) | Grade R3 (Alloying Grade) |
| Aluminum | 0.01% | 0.05% |
| Carbon | 0.02% | 0.03% |
| Chromium | 0.01% | 0.05% |
| Copper | 0.01% | – |
| Hydrogen | 0.00% | 0.01% |
| Iron | 0.05% | 0.08% |
| Molybdenum | 0.00% | – |
| Nickel | 0.01% | – |
| Niobium | 0.01% | – |
| Nitrogen | 0.01% | 0.02% |
| Oxygen | 0.04% | 0.13% |
| Silicon | 0.01% | 0.05% |
| Tantalum | 0.02% | – |
| Tin | 0.01% | – |
| Titanium | 0.01% | 0.05% |
| Tungsten | 0.02% | 0.02% |
| Uranium | 0.00% | – |
| Vanadium | 0.01% | – |
| Zirconium | Reportable | Reportable |
| Hafnium | Balance | Balance |
Mechanical Properties (Grade R1 – Rod)
| Condition | Test Temperature | Tensile Strength (min) | Yield Strength (min) | Elongation (min) |
| Annealed | Room Temperature | 58 ksi (400 MPa) | 22 ksi (150 MPa) | 22% |
| Annealed | 600°F (315°C) | 25 ksi (170 MPa) | 11 ksi (75 MPa) | 32% |
Technical Specifications
| Specification | Value |
| Standard | ASTM B737 Hot-Rolled and/or Cold-Finished Hafnium Rod, Wire and Particles |
| Grade | R1, R3 |
| Type | Rod, Wire and Particles |
| Size | Rod Dia: 6 – 120 mm, Length: ≤6000mmm Wire Dia: 0.5 – 9.5mm (Straight Wire, Coiled Wire, Coiled on Spools) Particle Dia: 6 – 25mm x Length 10-30mm |
| Condition & Finish | Hot-Rolled, Cold-Finished; clean and smooth surface finish |
| Inspection Certificate | EN 10204 Type 3.1 (Mill Test Certificate), EN 10204 Type 3.2 (Witness Testing or 3rd Party Inspection) |
| Test | Chemical Analysis, Tensile Test, Hardness Test, Nondestructive Testing (NDT) |
Packing
Packed in plywood boxes.
Applications
Grade R1 (Nuclear Grade)
Nuclear Reactor Components: Hafnium’s excellent neutron absorption properties make it highly valuable in the nuclear industry. Grade R1 is specifically designed for nuclear applications and used in control rods and neutron shielding components.
Neutron Absorbers: In nuclear reactors, hafnium absorbs neutrons and controls the fission process. This critical role helps maintain the balance of reactions within the reactor.
Safety Devices: Due to its neutron absorption capacity, hafnium is also used in safety devices within nuclear reactors to prevent accidental chain reactions.
Grade R3 (Alloying Grade)
High-temperature Alloys: Hafnium is added to nickel-based superalloys to improve strength and corrosion resistance at high temperatures, making these alloys ideal for turbine blades in jet engines and gas turbines.
Aerospace Materials: The high melting point and mechanical solid properties of hafnium-containing alloys make them suitable for aerospace applications, including space vehicle components where heat resistance is crucial.
Plasma Cutting Equipment: Hafnium is used in plasma torches for cutting and welding due to its excellent ability to emit electrons when heated, which enhances the efficiency of plasma cutting.
Applications of Both Grades
Chemical Industry: As part of the apparatus in aggressive or high-temperature chemical reactions due to hafnium’s corrosion resistance.
Electronic Equipment: In components where high temperature and corrosion resistance are needed.
Medical Devices: Particularly in radiation shielding components due to its neutron absorption capabilities.